- 182, Waghodia GIDC Gujarat 391760
- Monday - Friday : 10am - 6pm
Talk to Expert:02668 – 263555 / 263666
- Home
- WHAT IS FLUORO POLYMERS ?
WHAT IS FLUORO POLYMERS?
A Fluoropolymer is an organic compound consisting of fluorine and carbon atoms but can also contain oxygen or hydrogen. The atoms are held together by bonds to form monomers such as Tetra Fluoro Ethylene (TFE). When the monomer is polymerized they form into long chains to which TFE becomes polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Fluoropolymers can be either fully fluorinated or partially fluorinated.
1. FULLY FLUORINATED
PTFE (POLYTETRAFLUOROETHYLENE)
PFA (PERFLUOROALKOXY)
FEP (FLUORINATED ETHYLENE PROPYLENE)
2. PARTIALLY FLUORINATED
ETFE (ETHYLENE TETRAFLUOROETHYLENE POLYMER)
ECTFE (ETHYLENE CHLOROTRIFLUORO ETHYLENE POLYMER)
PVDF ( POLY VINYLIDENE FLUORIDE)
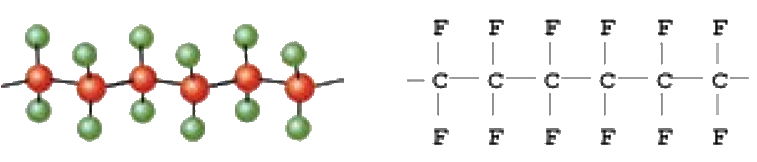
PTFE AT GLANCE
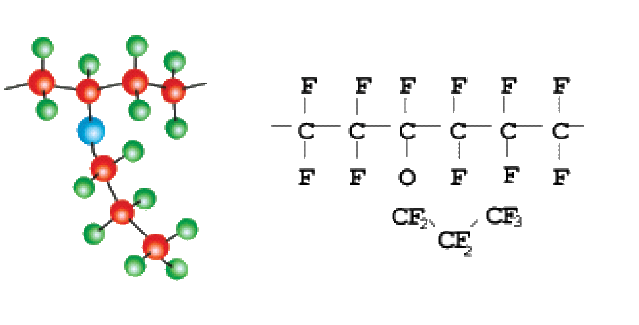
PTFE As you can see by the picture above all the carbon atoms are surrounded by fluorine atoms. Again, the strong carbon-fluorine bond leads to the high chemical resistance of this material.



We Believe build the Business
WE STANDS FOR
TRUST
TRANSPARENCY
ETHICAL PRACTICES
QUALITY CONSTRUCTION
TIMELY DELIVERY
CUSTOMER CENTRIC ATTITUDE
ENVIRONMENT CONCERN
INNOVATIVE PROCESS SOLUTIONS PVT. LTD
Recent Posts
-
Quality and Expertise: Best Leading B... May 24, 2023
-
DIP Pipe Manufacturer in India June 14, 2022
-
PTFE Products Manufacturers and Expor... February 17, 2022

